Also to be considered as a tax resident abroad, you must meet the following conditions:
The main objective of double tax agreements is to avoid double taxation of the same income by different states and to prevent tax evasion. Moreover, it is important to note that the principles set out in the treaties take precedence over the domestic law of the contracting states. These conventions will include the principles used to determine the taxpayer’s place of residence and the right of the State to tax certain income.
As far as double taxation is concerned, it generally concerns individuals or companies that reside and operate in several countries. Thus, two different jurisdictions may tax the same income under their own domestic laws. To this end, double tax agreements regulate this phenomenon so that the income concerned is taxed only once. As a result, the taxpayer may be granted relief from paying tax on the same income by means of a tax exemption or tax credit.
Thus, where a person is considered to be a resident of Contracting States, double tax agreements provides criteria that prevail over those of domestic law for determining the residence of the taxpayer concerned. The criteria may differ from treaty to treaty, so you should refer to the treaty applicable to your situation.
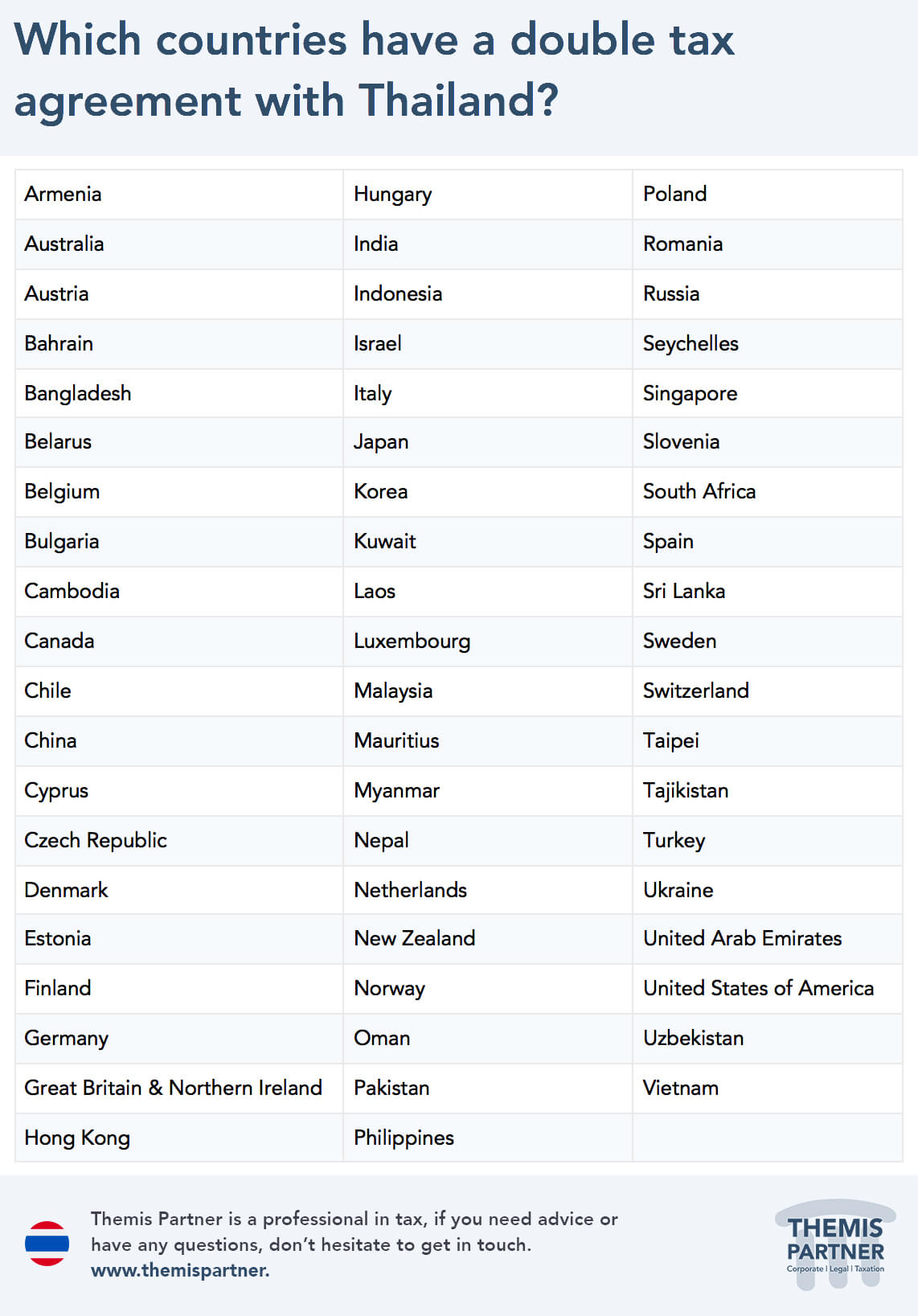
For this purpose, Thailand currently has 61 double tax agreements with the following states:
In the context where a person meets the tax residence criteria of two states, double taxation treaties generally provide for the following qualification rules:
The concept of a permanent establishment is essential in determining whether industrial or commercial activities carried on in a state other than that of the residence of the corporation are taxable at the place of residence or, on the contrary, at the place where those activities are carried on.
The concept of permanent establishment generally refers to a fixed place of business with its own activities in a State or a dependent agent with the power to bind the company. Each agreement has a specific definition of permanent establishment, so reference should be made to it.
Generally speaking, the term refers to the fixed place of business of the company which includes the following:
In addition, double tax agreement generally indicate what does not qualify as a permanent establishment.
In the convention signed between other countries and Thailand, are not permanent establishments if the facility:
Determination of tax residence is only a first step. In fact, double taxation agreements will generally allow either a tax exemption or a tax credit that corresponds to the methods of eliminating double taxation.
Thus, if you receive income from one country while living in another, you will not have to pay the same taxes in both countries. As mentioned before, the main purpose of double taxation agreements is to avoid this. Each double tax agreement sets out different methods of eliminating double taxation depending on the country.
The first method is the tax exemption method. The country of residence does not tax income that, according to the double tax treaty, is taxed in the source country.
The second method is the tax credit method. The resident country has the right to tax income that has already been taxed in the source country. It calculates the tax on the basis of the taxpayer’s total income, including income from the other country, which, according to the double taxation agreement, is taxed in that other country. However, it allows a deduction for the tax paid in the source country.
Tax agreements generally provide that when tax is due to more than one country on the same income, the second country must provide a tax credit for the taxes paid in the first country.
In conclusion, knowing the mechanisms of international taxation is essential. Double tax agreements are part of this scheme and offer many advantages, including a tax reduction by eliminating double taxation. However, it is important to understand the functioning of these conventions in order to take advantage of their benefits. Furthermore, it is imperative not to miss deadlines with the tax authorities in order to fully benefit from the double taxation treaties and avoid any penalties or late fees.