Ready to fill official form
Includes PIT Guide
Last update in 2024
Ready to fill official form
Includes PIT Guide
Last update in 2024
Home › Accounting services › Personal income tax
Learn more about Personal Income Tax
Income tax, also called Personal Income Tax (PIT) in Thailand, is a direct tax on all income a person receives. By person, we mean a natural person, a partnership, a company without legal personality, an undivided heritage between several people or a deceased. Taxpayers are classified as residents or non-residents based on length of stay in Thai territory. In general, a person subject to Personal Income Tax must calculate their tax liability, complete their tax return and pay tax, if any, accordingly on a calendar year basis. The amount of Personal Income Tax payable is calculated based on progressive rates provided for by the Thai tax code. The tax return as well as the tax payment must be submitted to the Revenue Department no later than March 31 following the taxable year.
Table of contents
-
Who is subject to income tax in Thailand?
-
Can the tax non-resident be subject to income tax?
-
What is the taxable income?
-
How is taxable income calculated?
-
What are the possible deductions applicable?
-
What are the tax rates applicable to the progressive system?
-
What are the incomes that can opt for autonomous taxation not subject to the progressive regime?
-
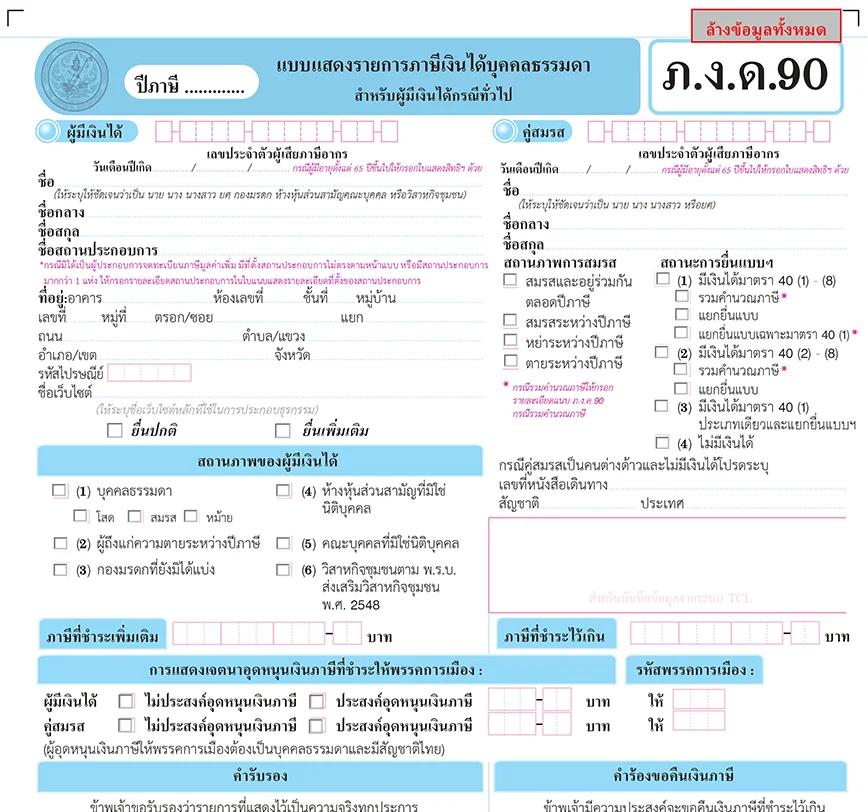
How to make an income tax declaration?
-
When is it possible to benefit from a tax credit?
-
What is the Tax ID number?
-
What are the penalties for late or failure to declare?
-
I have income from Thai real estate and live abroad, do I have to report in Thailand?
Who is subject to Personal Income Tax in Thailand?
Income taxpayers in Thailand fall into two categories: residents and non-residents. The term resident refers to any person residing in Thailand for one or more periods totaling more than 180 days in a fiscal year.
The resident is required to pay tax on all income received in Thailand as well as income from foreign sources but brought into Thailand.
However, the non-resident is only taxed on income received in Thailand, whether income from employment in Thailand, land income from property located in Thailand or income from securities received in Thailand reason for owning shares or shares in a Thai company.
Can the tax non-resident be subject to income tax?
In principle, the tax non-resident is taxed in the country where he holds the status of resident. However, as soon as he receives income from Thailand, it will be taxed in accordance with the Personal Income Tax not governed by the provisions of the Thai Tax Code.
Many bilateral tax treaties between Thailand and third countries have been signed in order to avoid double taxation of taxpayers thus allowing a tax credit on their return.
What is the taxable income?
Residents and non-residents are taxed on their assessable income from employment or any activity carried on in Thailand. Article 40 of the Thai Tax Code provides for eight categories of taxable income:
1. Salaries and wages (including income from stock options, housing allowances and other social benefits).
2. Income from hiring a job, placement office or service rendered.
3. Income from goodwill, copyright, franchise, patent, other rights, rent, etc.
4. Interest income, dividends, bonuses for investors, merger gains, acquisition or dissolution of a company or association, gain on disposal of shares, cryptocurrency ect.
5. Income from the rental of real estate, breach of a hire purchase contract and installment sale.
6. Income from liberal professions in the fields of law, medicine, engineering, architecture, accountancy and fine arts.
7. Income from an employment contract whereby the contractor provides essential materials other than tools.
8. Income from business, commerce, industry and income other than those specified under Wages and salaries with income from an employment contract.
How is taxable income calculated?
Taxable income can be defined as the sum of annual income deducted from deductions and allowances provided for according to the category of income selected.
To calculate the taxable income, it is necessary to proceed in different successive stages:
| ➤ Distribute the income you have received between the 8 income categories mentioned above |
| ➤ The exemption regime provided for by said income category must be applied (table below) |
| ➤ You should then add up all the income you received after applying the deductions |
| ➤ It is now possible to determine the taxable income after having subtracted the allowances from your family quotient. In fact, you benefit from an automatic deduction on your taxable income of: - 60,000 THB as a taxpayer - 60,000 THB for your wife if she has no income - 30,000 THB for each of your children under certain conditions |